|
ČESKÁ TECHNICKÁ NORMA |
|
ICS 35.240.40 |
|
Prosinec 1997 |

|
Bankovnictví - |
ČSN 97 9114 |
|
|
|
|
Banking - Key management (retail) - Part 3: Key life cycle for symmetric ciphers
Banque - Gestion de clés (services aux particuliers) - Partie 3: Cycle de vie des clés pour les algorithmes cryptographiques symétriques
Bankwesen - Schlüsselverwaltung (Einzelhandel) - Teil 3: Schlüsselzyklus für symmetrische Verschlüsselungen
Tato norma přejímá anglickou verzi evropské normy EN ISO 11568-3:1994. Evropská norma EN ISO 11568-3:1994 má status české technické normy.
This standard implements the English version of the European Standard EN ISO 11568-3:1994. The European Standard EN ISO 11568-3:1994 has the status of a Czech Standard.
Anotace obsahu
Tato část normy ČSN EN ISO 11568 specifikuje pro prostředí bankovních služeb pro drobnou klientelu požadavky bezpečnosti a metody implementace pro každý krok životního cyklu klíče.
Životní cyklus klíče je aplikován na klíče na všech úrovních hierarchie klíčů.
Systém je použitelný pro libovolnou organizaci, která je zodpovědná za ochranu klíčů, které se používají vsymetrické šifře.
Tato část normy ČSN EN ISO 11568 je použitelná v institucích, které jsou zodpovědné za implementační techniky správy klíčů užívaných k ochraně dat při transakcích prováděných prostřednictvím bankovních karet.
Nahrazení předchozích norem
Tato norma nahrazuje ČSN EN ISO 11568-3 (97 9114) Bankovnictví- Správa klíčů (bankovní služby pro drobnou klientelu) - Část 3:
Životní cyklus klíče pro symetrickou šifru z prosince 1996.
Ó Český normalizační institut, 1997
|
|
|
50204 |
Národní předmluva
Struktura normy
ČSN EN ISO 11568 po hlavním názvem Bankovnictví - Správa klíčů (bankovní služby pro drobnou klientelu) se skládá z následujících částí:
- Část 1: Úvod do správy klíčů
- Část 2: Techniky správy klíčů pro symetrickou šifru
- Část 3: Životní cyklus klíče pro symetrickou šifru
- Část 4: Techniky správy klíčů pro asymetrickou šifru
- Část 5: Životní cyklus klíče pro asymetrickou šifru
- Část 6: Schémata pro správu klíčů
Změny proti předchozí normě
Proti předchozí normě dochází ke změně způsobu převzetí EN ISO 11568-3:1996 do soustavy norem ČSN. Zatímco ČSN EN ISO 11568-3 z prosince 1996 převzala EN ISO 11568-3:1996 schválením k přímému používání jako ČSN, tato norma ji přejímá převzetím originálu s překladem úvodní části normy.
Citované normy
ISO 8908:1993 zavedena v ČSN ISO 8908 Bankovnictví a související bankovní služby - Slovník a datové prvky (97 9118) ISO/IEC 10116:1991 zavedena v ČSN ISO/IEC 10116 Informační technologie - Módy činnosti pro algoritmus n-bitové blokové šifry (36 9742)
ISO 9564-1:1991 zavedena v ČSN ISO 9564-1 Bankovnictví - Řízení a bezpečnost osobních identifikačních čísel - Část 1: Principy a techniky ochrany PIN (97 9118)
ISO 11568-1:1994 zavedena v ČSN EN ISO 11568-1 Bankovnictví - Správa klíčů (bankovní služby pro drobnou klientelu) - Část 1: Úvod do správy klíčů (97 9194)
ISO 11568-2:1994 zavedena v ČSN EN ISO 11568-2 Bankovnictví - Správa klíčů (bankovní služby pro drobnou klientelu) - Část 2: Techniky správy klíčů pro symetrickou šifru (97 9194)
Vypracování normy
Zpracovatel: INFO 7 Praha, IČO: 44266154, Ing. Jiří Roleček,
Technická normalizační komise: TNK 42 Výměna dat
Pracovník Českého normalizačního institutu: Ing. Petr Wallenfels
|
EVROPSKÁ NORMA |
EN ISO 11568-3 |
|
EUROPEAN STANDARD |
Červen 1996 |
|
NORME EUROPÉENNE |
|
|
EUROPÄISCHE NORM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICS 35 100
Deskriptory: viz ISO norma
Bankovnictví - Správa klíčů (bankovní služby pro drobnou klientelu) - Část 3: Životní cyklus klíče pro symetrickou šifru (ISO 11568-3:1994)
Banking - Key management (retail) - Part 3: Key life cycle for symmetric ciphers(ISO 11568-3:1994)
Banque - Gestion de clés (services aux particuliers) - Partie 3: Cycle de vie des clés pour les algorithmes cryptographiques symétriques(ISO 11568-3:1994)
Bankwesen - Schlüsselverwaltung (Einzelhandel) - Teil 3: Schlüsselzyklus für symmetrische Verschlüsselungen (ISO 11568-3:1994)
Tato evropská norma byla schválena CEN
Členové CEN jsou povinni splnit požadavky Vnitřních předpisů CEN/CENELEC, v nichž jsou stanoveny podmínky, za kterých se této evropské normě bez jakýchkoliv modifikací uděluje statut národní normy.
Aktualizované seznamy a bibliografické citace týkající se těchto národních norem lze vyžádat v Ústředím sekretariátu CEN nebo u každého člena CEN.
Tato evropská norma existuje ve třech oficiálních verzích (anglické, francouzské, německé). Verze v každém jiném jazyce přeložená členem CEN do jeho vlastního jazyka, a kterou notifikuje Ústřednímu sekretariátu CEN, má stejný status jako oficiální verze.
Členy CEN jsou národní normalizační orgány Belgie, České republiky, Dánska, Finska, Francie, Irska, Islandu, Itálie, Lucemburska, Německa, Nizozemska, Norska, Portugalska, Rakouska, Řecka, Spojeného království, Španělska, Švédska a Švýcarska.
CEN
Evropská komise pro normalizaci
European Committee for Standardization
Comité Européen de Normalisation
Europäisches Komitee für Normung
Ústřední sekretariát: rue de Strassart 36, B-1050 Brussels
Předmluva
Text mezinárodní normy vypracovaný v technické komisi ISO/TC 68 „Bankovnictví a související finanční služby" Mezinárodní organizace pro normalizaci (ISO) byl převzat jako evropská norma technickou komisí CEN/TC 224 „Strojem čitelné karty, související rozhraní a postupy", sekretariátem při AFNOR.
Této evropské normě musí být udělen status národní normy buď vydáním identického textu, nebo schválením k přímému používání nejpozději do prosince 1996 a konfliktní národní normy musí být zrušeny nejpozději do prosince 1996.
V souladu s Vnitřními předpisy CEN/CENELEC se následující země zavazují, že zavedou tuto evropskou normu: Belgie, Česká republika, Dánsko, Finsko, Francie, Irsko, Island, Itálie, Lucembursko, Německo, Nizozemsko, Norsko, Portugalsko, Rakousko, Řecko, Spojené království, Španělsko, Švédsko a Švýcarsko.
Oznámení o schválení
Text mezinárodní normy ISO 11568-3:1994 byl schválen CEN jako evropská norma bez jakýchkoliv modifikací.
|
INTERNATIONAL |
ISO |
|
STANDARD |
11568-3 |
|
|
First edition |
|
|
1994-12-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Banking - Key management (retail) -
Part 3:
Key life cycle for symmetric ciphers
Banque - Gestion de clés (services aux particuliers) -
Partie 3: Cycle de vie des clés pour les algorithmes cryptographiques
symétriques

Reference number
ISO 11568-3:1994(E)
Obsah |
|
strana |
Contents |
Page |
|
1 |
Scope |
1 |
2 |
Normative references |
1 |
3 |
Definitions |
1 |
4 |
Requirements |
2 |
4.1 |
Key generation |
2 |
4.2 |
Key storage |
2 |
4.3 |
Key retrieval from back up |
3 |
4.4 |
Key distribution loading |
3 |
4.5 |
Key use |
3 |
4.6 |
Key replacement |
3 |
4.7 |
Key destruction |
4 |
4.8 |
Key deletion |
4 |
4.9 |
Key archive |
4 |
4.10 |
Key termination |
5 |
5 |
Methods |
5 |
5.1 |
Key generation |
5 |
5.2 |
Key storage |
5 |
5.3 |
Key retrieval from back up |
5 |
5.4 |
Key distribution and loading |
5 |
5.5 |
Key use |
7 |
5.6 |
Key replacement |
7 |
5.7 |
Key destruction |
7 |
5.8 |
Key deletion |
7 |
5.9 |
Key archive |
7 |
5.10 |
Key termination |
8 |
Ó ISO 1994
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any from or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 · CH-1211 Genčve 20 · Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a world-wide federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting a vote.
International Standard ISO 11568-3 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 68, Banking and related financial services, Subcommittee SC 6, Financial transaction cards, related media and operations.
ISO 11568 consists of the following parts, under the general title Banking - Key management (retail):
- Part 1: Introduction to key management
- Part 2: Key management techniques for symmetric ciphers
- Part 3: Key life cycle for symmetric ciphers
- Part 4: Key management techniques for asymmetric ciphers
- Part 5: Key life cycle for asymmetric ciphers
- Part 6: Key management schemes
Introduction
ISO 11568 is one of a series of standards describing procedures for the secure management of the cryptographic keys used to protect messages in a retail banking environment, for instance, messages between an acquirer and a card acceptor, or an acquirer and a card issuer. Key management of keys used in an integrated circuit card (ICC) environment is not covered by ISO 11568.
Whereas key management in a wholesale banking environment is characterized by the exchange of keys in a relatively high-security environment, this standard addresses the key management requirements that are applicable in the accessible domain of retail banking services. Typical of such services are point-of-sale/point-of-service (POS) debit and credit authorization and automated teller machine (ATM) transaction.
This part this ISO 11568 describes the key life cycle in the secure management of cryptographic keys for symmetric ciphers. It states both requirements and implementation methods for each step in the life of such a key, utilizing the key management principles, services and techniques describet in ISO 11568-1 and ISO 11568-2.
The key life cycle consists of three phases:
a) Pre-use: during which the key is generated.
b) Use: during which the key is distributed amongst communicating parties for operational use.
In a process where both communicating parties contribute to the generation of a new key, key generation and distribution are closely integrated.
Some key management schemes are designed for transforming keys automatically during operational use.
c) Post-use: during which a key is archived or terminated.
Figure 0.1 gives a schematic overview of the key life cycle. It shows how a given operation on a key changes its state.
A key is considered to be a single object of which multiple instances can exist at different locations and in different forms. A clear distinction is made between the following operations:
- destruction of a single key instance;
- deletion of a key from a given location, which implies destruction of all instances of this key at that location.
- termination of a key; which implies deletion of the key from all locations.
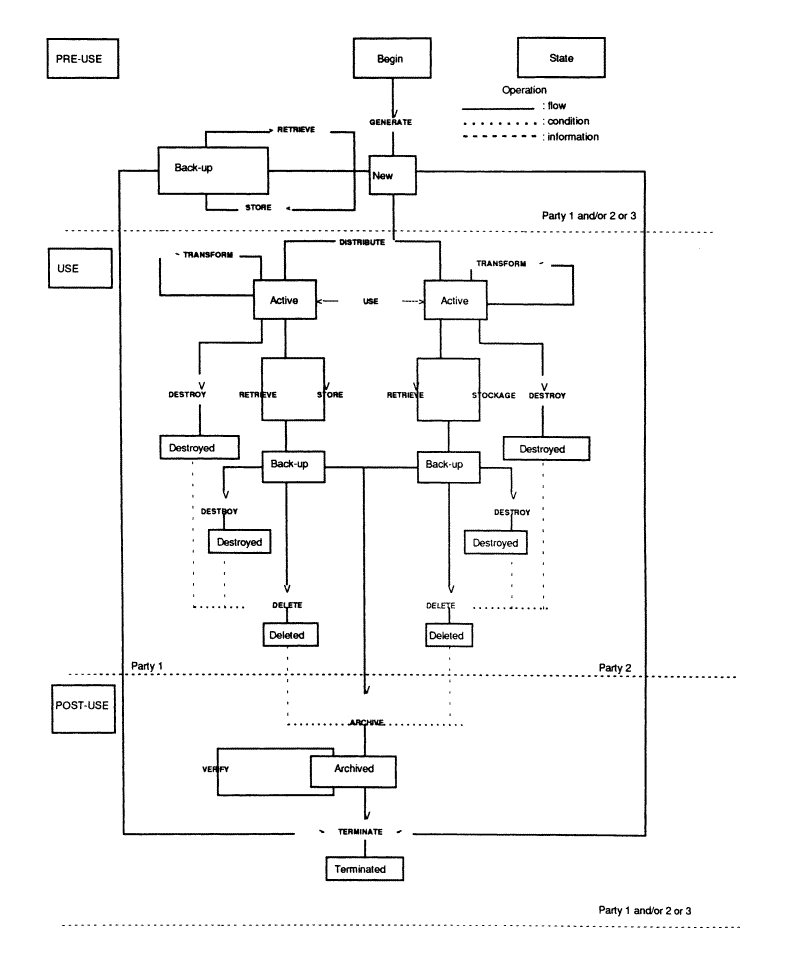
Figure 0.1 - Key life cycle
Prázdná strana!
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD Ó ISO ISO 11568-3:1994(E)
Banking - Key management (retail) -
Part 3:
Key life cycle for symmetric ciphers
1 Scope
This part of ISO 11568 specifies for the retail banking environment the security requirements and the implementation methods for each step in the key life cycle.
The key life cycle applies to keys at all levels of a key hierarchy.
It is applicable to any organisation that is responsible for the protection of keys used in a symmetric cipher.
This part of ISO 11568 is applicable to institutions responsible for implementing techniques for the management of keys used to protect data in bank card originated transaction.
-- Vynechaný text --
Zdroj: www.cni.cz